Disclosure: some of the links below are affiliate links. This means that Revealed Films may earn from qualifying purchases or clicks. *
We’ve been talking about getting a “Clean Sweep” for the new year… so far, we’ve covered Detox and Diet. In the last post, we shared about the Whole30 diet, which is excellent for hitting the “reset” button.
But what if you’re dealing with stubborn pain and inflammation? Whole30 is a good start, but if you’re ready to go deeper and turn on your body’s natural ability to fight inflammation and start healing?
Keto is something you should look into.
Dr. Jockers is a world-renowned expert on the Keto Diet, and he’s agreed to share 3 guest posts with the Pain Revealed community here. There’s a lot of information to take in, but you’ll learn the reason why keto works so well to reduce painful inflammation and give your body a chance to truly heal. Dr. Jockers Here’s the first article on Keto:
Keto Autoimmune Diet: Burn Fat and Inflammation
by Dr. David Jockers
Autoimmune conditions occur when the body’s immune system turns against itself. As the prevalence of autoimmune conditions continues to rise, people are looking to natural strategies to prevent and improve these conditions. Implementing a keto autoimmune diet is a fantastic way to combat autoimmunity.
The keto autoimmune diet is a 6-week autoimmune elimination diet following ketogenic guidelines. With the keto autoimmune diet, the most common immune provoking foods are removed along with toxic, highly inflammatory foods. These foods are replaced with healthy fats, organic low-carbohydrate vegetables and low-glycemic fruits, herbs, grass-fed organic meats and eggs, and wild-caught fish.
The keto autoimmune diet will decrease inflammation which is common in autoimmune conditions. It can also balance your blood sugar, help you to lose excess weight, improve your energy, and improve your cognitive function. By eliminating foods that may be triggering an immune response and giving your body time to heal, autoimmune conditions may improve or even be prevented.
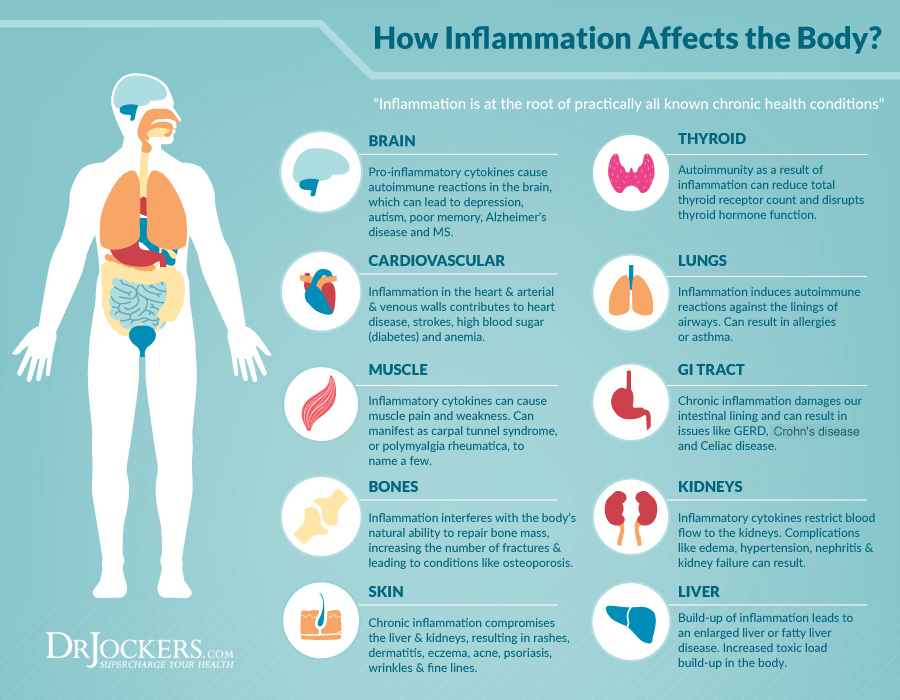
What is an Autoimmune Condition?
An autoimmune condition occurs when the body’s immune system malfunctions. It mistakenly identifies healthy cells and tissues as foreign invaders and starts attacking and destroying them. This can happen in almost any part of the body, including the brain, muscles, skin, and other organs.
Autoimmune conditions are usually chronic and may be life threatening. There are two general categories of autoimmune diseases: organ-specific (such as type 1 diabetes) and systemic varieties (which occur when the immune system attacks multiple organs and tissues). In addition to type 1 diabetes, other examples of autoimmune conditions are rheumatoid arthritis, Graves, Hashimoto’s, Lupus, Crohn’s, ulcerative colitis, psoriasis, multiple sclerosis, scleroderma, and Sjogren’s.
It is estimated that 23.5 million (and up to 50 million) Americans have an autoimmune disease (1). Researchers have identified 80-100 autoimmune diseases, and at least 40 more diseases that may have an autoimmune basis.
Around 80% of people with autoimmune conditions are women. In fact, they are one of the 10 leading causes of death for girls and women in all age groups (up to 64 years of age).
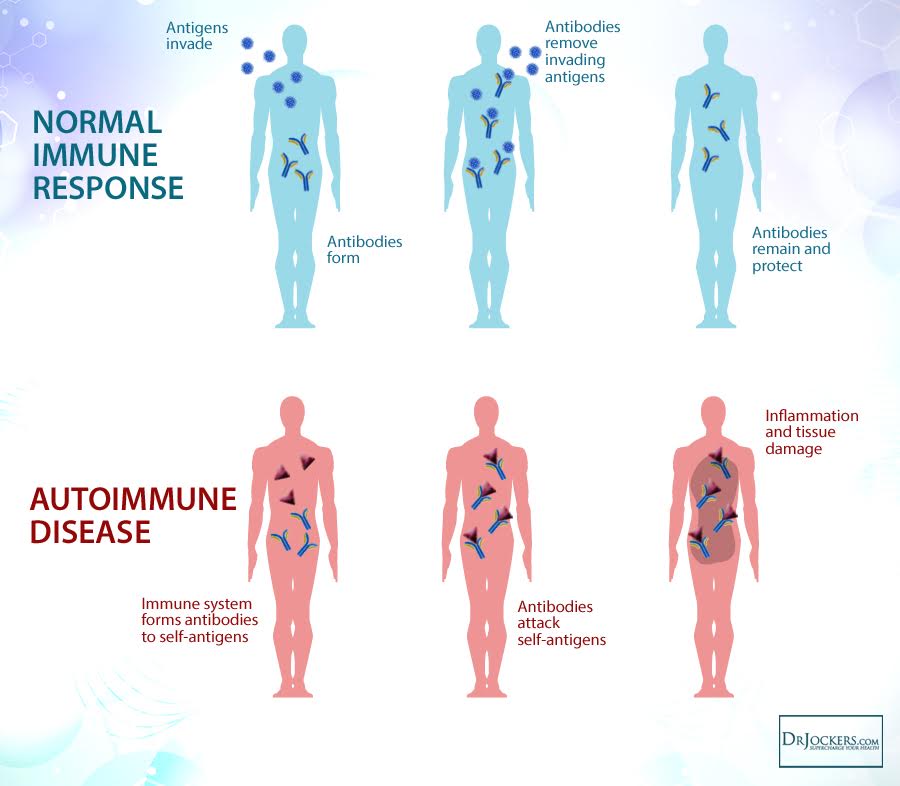
Causes of Autoimmune Conditions
The cause of autoimmunity is not clear. Research suggests there may be a genetic susceptibility to autoimmunity and different environmental triggers that bring on the condition (2). In fact, around 75% of autoimmune conditions are caused by environmental factors.
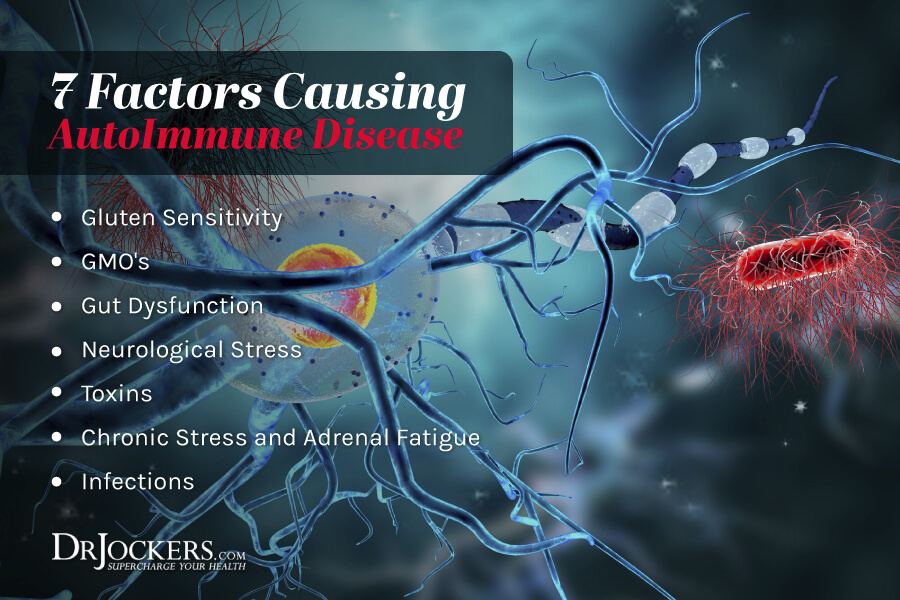
The 7 major causes of autoimmunity are:
- Gluten Sensitivity
- Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs)
- Gut Dysfunction
- Neurological Stress
- Toxins
- Stress and Hormones
- Infections
Many of these factors destroy the bacteria in the gut. These bacteria heavily regulate the immune system. In fact, 70% of your immune system resides in the gut.
The cells that line the digestive tract are only one layer thick. When those cells or the links between them are damaged, the layer becomes porous and the immune system is exposed to the foods and other things that you are consuming. Food sensitivities can damage this lining, and a damaged lining can result in food sensitivities. This is a critical factor in many autoimmune conditions.
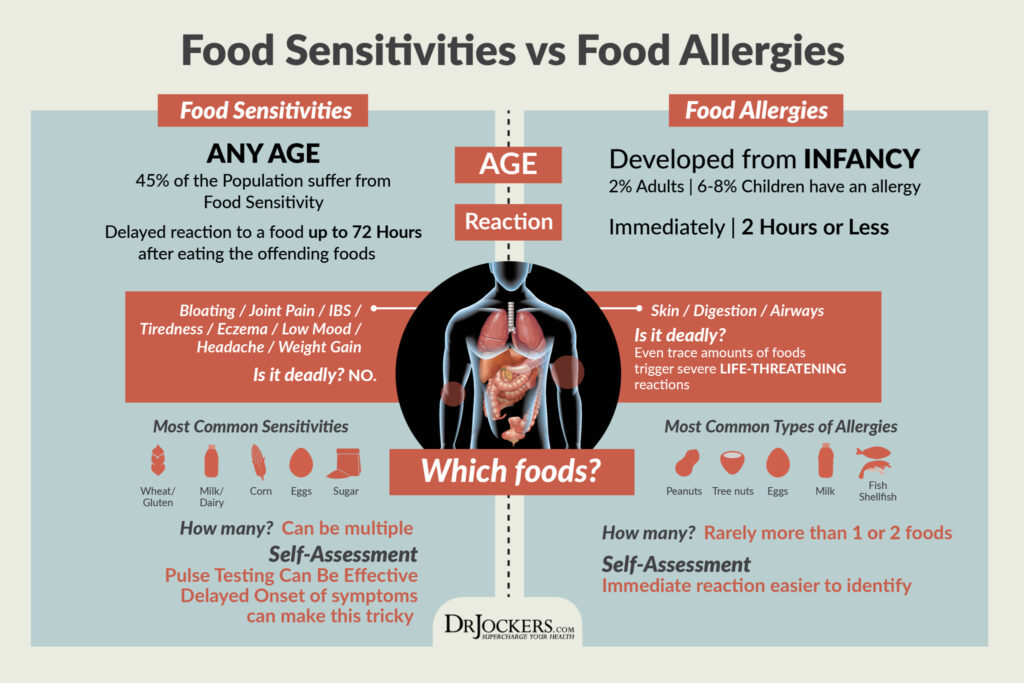
Food Sensitivities and Autoimmunity
A food sensitivity is an immune-mediated response to certain foods. When you have food sensitivities, your immune system reacts to certain foods as a threat amplifying the immune response.
It is estimated that 45-75% of individuals have food sensitives. Repeated exposure to the foods causes inflammation and other health problems. The consequences of food-induced immune system activation can be subtle initially, but may become serious over time.
A recent observational study found a clear difference in food sensitivity profiles for people with autoimmune diseases (3). IgG levels for specific food antibodies were significantly higher in patients with autoimmune conditions which means they had a greater immune reaction to these foods.
Food sensitivities can be hard to identify. This is because symptoms of food sensitives are usually delayed up to 72 hours after consuming the offending food. These symptoms are not exclusively related to the gut, and can include migraines, fatigue, joint pain, skin issues, and many others. It is important to remove foods that may be causing an immune response to prevent and improve autoimmune conditions.
Benefits of the Ketogenic Diet for Autoimmune Conditions
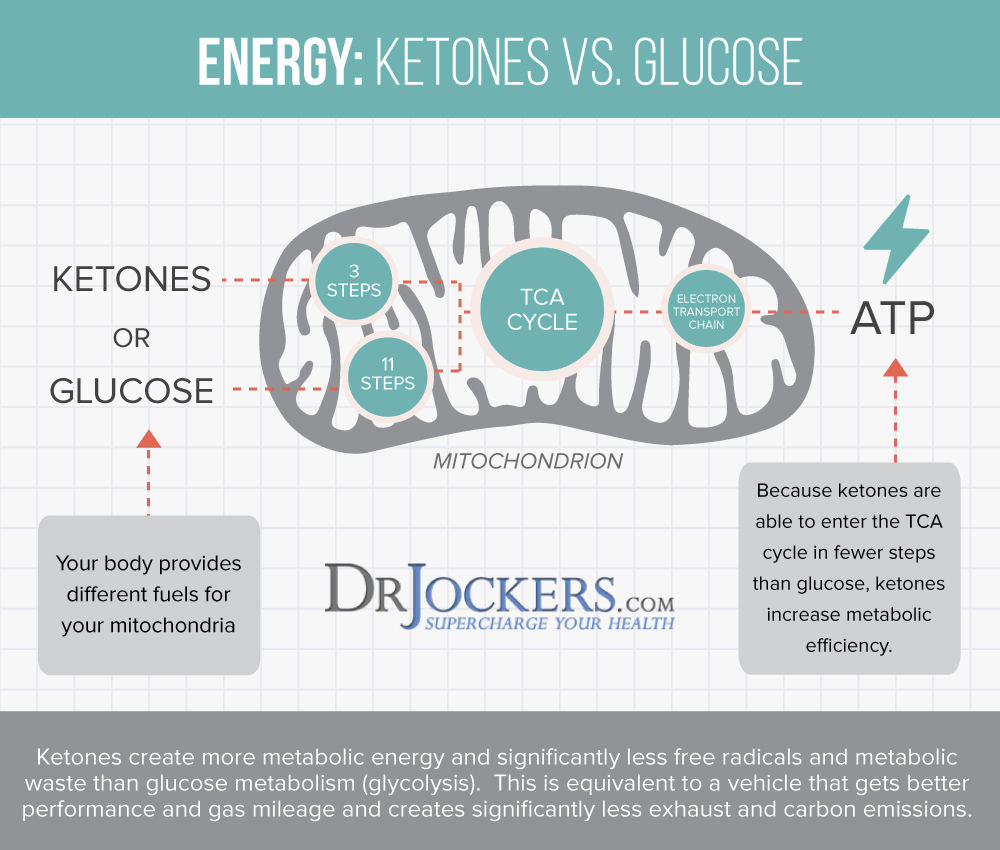
The ketogenic diet is a nutrition and lifestyle plan that helps your body use fat (stored fat and dietary fat) rather than sugar for fuel. When the body is in ketosis, it utilizes ketones as an energy source instead of sugar.
Transitioning from a sugar burner to a fat burner with a keto autoimmune diet can have amazing benefits for people with autoimmune conditions. The ketogenic diet lowers inflammation, balances blood sugar levels and your mood, improves mental performance, gives you energy, ends cravings, helps you lose excess weight and controls weight gain, and reduces your risk of chronic disease (4).
A major contributor to autoimmune conditions is inflammation. The ketogenic diet lowers inflammation by reducing the amount of free radical production, stabilizing blood sugar levels, and reducing insulin levels. With lower levels of inflammation and stabilized blood sugar levels, your mitochondria will produce more of the energy carrying molecule Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP).

Mitochondria and Autoimmunity
Mitochondria are the energy powerhouses of your cells. Along with producing ATP, they maintain glutathione levels, protect DNA, signal cell reproduction, activate cell apoptosis, and maintain cell electrochemical integrity.
Mitochondrial impairment is a key factor in inflammation and many autoimmune diseases appear to have a mitochondrial basis (5). The ketogenic diet stimulates the growth of new and stronger mitochondria, which is important for preventing and improving autoimmune conditions.
By reducing inflammation and improving mitochondrial function, the ketogenic diet allows the body to heal and mitigate disease processes more effectively. This improves your risk factors for autoimmune diseases, gives you optimal energy production, and creates an efficiently functioning body.
The ketogenic diet is also neuroprotective. Studies show that the ketogenic diet has therapeutic potential for treating the neurodegenerative component of multiple sclerosis (MS) (6). Ketones provide steady, clean fuel to energize brain cells and protect against cell death. This could benefit people with MS and other autoimmune conditions.
How to Implement a Ketogenic Autoimmune Diet
The keto autoimmune diet is a high fat, moderate protein, low carbohydrate diet that eliminates specific foods for a 6-week period. For the foods included in the diet, you will follow ketogenic diet guidelines: 70-80% of calories from fat, 15-20% from protein, and 5-10% from carbohydrates.
The foods eliminated on the keto autoimmune diet are the most common allergenic/sensitivity foods which may be contributing to or causing a negative reaction and inflammation. The goal in eliminating these foods is to identify foods that may be contributing to your autoimmune condition.
After the elimination period, you slowly reintroduce foods, one at a time, noting any reactions and symptoms you may experience. It is important to keep a journal during the entire process to document how you are feeling as you eliminate and reintroduce the foods.

Keto AutoImmune Foods Included
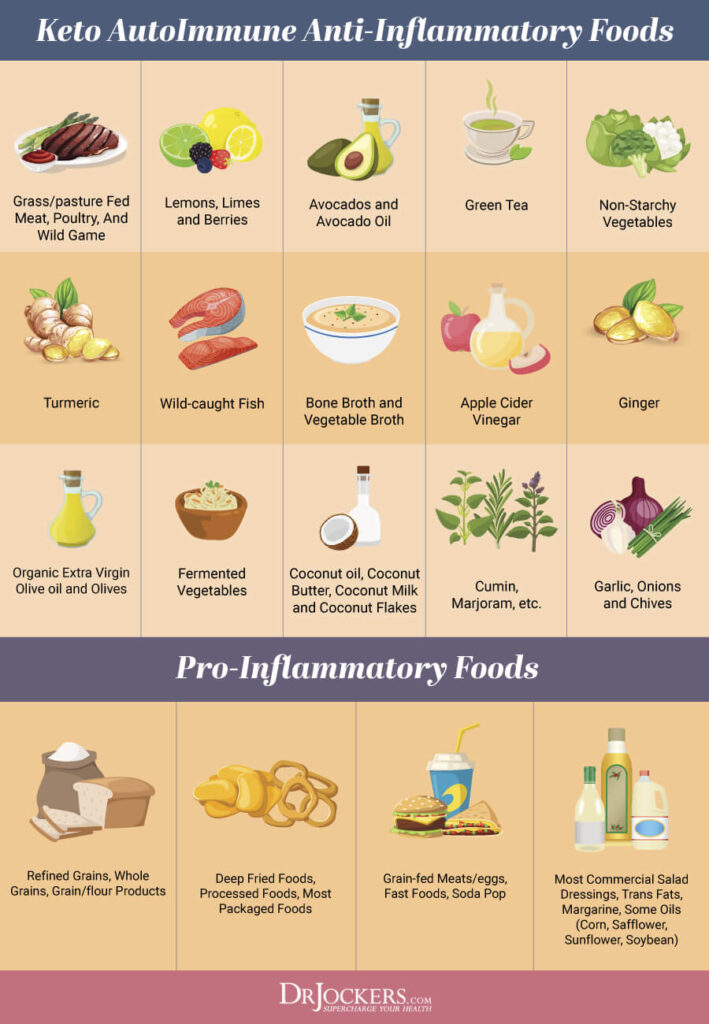
Foods included in the keto autoimmune diet include healthy fats, clean-sourced protein and low carbohydrate vegetables, low glycemic fruits, and herbs. These foods help to reduce inflammation and support the immune system.
One very important strategy is to be sure to get the highest quality nutrient dense foods that have the minimal amount of environmental toxins. In particular, look for organic foods as much as possible because pesticides have been linked to autoimmune conditions (7).

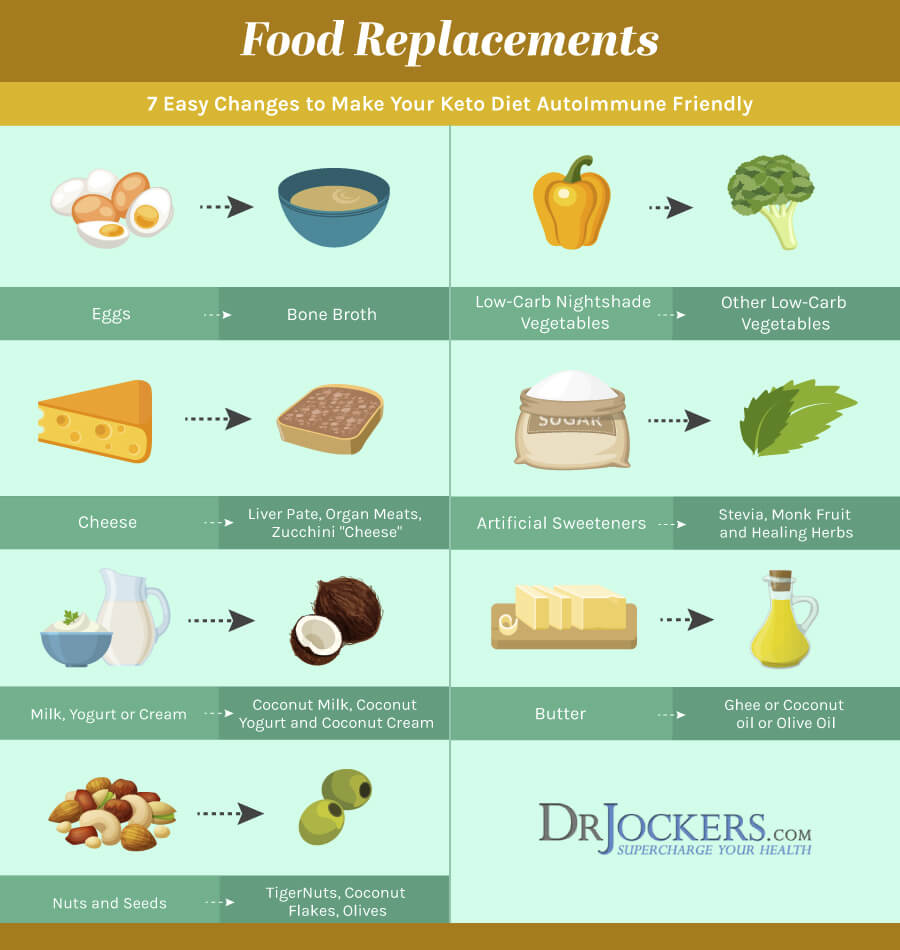
Healthy Fats
Consuming plenty of healthy fats is very important on the keto autoimmune diet. Healthy fats are found in coconut, olives, avocados, and their oils and in grass-fed butter and ghee. Pumpkin, flax, hemp and chia seeds, and borage, hemp or flax oils are additional sources of good fats.
Omega-3 fatty acids and conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) found in wild-caught salmon and grass-fed beef and dairy have many health benefits. These healthy fats are an efficient source of fuel for the body to combat inflammation.

Clean Protein
Great protein sources are grass-fed, pasture-raised, and organic meats. Beef, bison, lamb, buffalo, venison, chicken, pheasant, duck and turkey are all included. Wild-caught fish such as Alaskan Sockeye salmon is an excellent choice.
I am a big fan of organic bone broth or collagen proteins to use which provide the type of protein that helps make up your connective tissue and joints. In addition, hypoallergenic pea proteins can be used as well as beef protein from clean-sourced animals.
Low Carbohydrate Vegetables, Low-Glycemic Fruits and Herbs
A variety of lower-carbohydrate, low-glycemic, colorful vegetables and fruits should be included for their abundant antioxidants and phytonutrients. Examples are cruciferous vegetables, cucumbers, asparagus, and leafy greens. Low-glycemic fruits to include on the keto autoimmune diet are berries, lemons and limes, grapefruits, gogi berries, avocados, coconuts, and granny smith apples.
I am a huge fan of carminative herbs like rosemary, oregano, basil, cilantro, sage, and thyme. These carminatives have healing properties and they help to improve overall digestive health and should be included in the keto autoimmune diet. Spices and sweeteners like cinnamon, garlic, ginger, turmeric, pink salt, stevia, and monk fruit are included. However, cayenne and paprika should not be used on the keto autoimmune diet.

Other Keto AutoImmune Foods to Include
Fermented foods and teas are excellent to include on the keto autoimmune diet. Organic green tea and organic herbal teas like ginger, Pau D Arco, and Nighty Night are great choices.
Fermented foods should be made without nightshade vegetables. These include coconut milk kefir or yogurt, fermented vegetables, kombucha, coconut water kefir, kimchi, and sauerkraut. Coconut milk, yogurt and kefir are fantastic dairy substitutes.
Other coconut products like coconut butter, coconut flour, and unsweetened coconut flakes are included on this diet, as well as flax crackers and organic raw apple cider vinegar.

Foods Excluded
The keto autoimmune diet eliminates foods that most commonly cause an immune response and additional highly pro-inflammatory foods. The foods you should eliminate include gluten, dairy, eggs, peanuts, tree nuts, soy, wheat, fish and shellfish.
Many people are sensitive to nightshade vegetables (tomatoes, potatoes, eggplant, bell peppers), corn, legumes, all grains, processed foods, and vegetable oils. These foods should also be eliminated.
In addition to these foods, it is important to eliminate foods that cause inflammation. These include:
- Sugar
- Refined carbohydrates (white flour, white rice, white potatoes)
- Conventionally-raised meat and dairy
- Farm-raised fish
- Processed meats
- Trans fats (partially hydrogenated oils)
- Mono-sodium Glutamate (MSG) and other food additives and preservatives
- Highly processed vegetable and seed oils, such as canola, corn, sunflower, peanut, grapeseed, cottonseed, and safflower
- Artificial Sweeteners.
These foods upregulate inflammation, and create extra acidity in the tissues.
Other Foods that May be Problematic
You may have sensitivities to the foods that are allowed on the elimination diet such as citrus fruits, seeds, berries, onions, and certain meats. Higher FODMAP foods can also cause digestive symptoms in some people. It is important to recognize any unwanted symptoms such as noticeable gas, bloating, altered bowel habits, fatigue, increased pain and inflammation, eczema, acne, insomnia, anxiety, brain fog, and mood changes that are associated with any foods.
It is also important to note that when you have leaky gut, food sensitivities can develop to the foods you consume most often as discussed above. It is critical to avoid any foods that may be inflaming the gut. This allows the gut time to heal. Once your gut heals, you may be able to eat these foods again without a sensitivity or immune response.
Reintroducing Foods
When you are ready to reintroduce foods, it is good to follow a schedule. The recommended reintroduction schedule is:
- Bell peppers
- Almonds and almond butter
- Walnuts
- Pecans
- Brazil nuts
- Pistachios
- Cashews
- Pasture-raised egg yolk
- Pasture-raised egg white
- Grass-fed yogurt or cheese
Slowly reintroduce foods, one at a time, noting any reactions and symptoms you may experience. If you experience any negative symptom, then continue to avoid that food for a longer period. You can learn more about how to do pulse biofeedback testing and food reintroduction in this article.

Transitioning to a Keto Autoimmune Diet
If you are new to a low-carbohydrate lifestyle, it is helpful to slowly transition to a high fat, low carbohydrate ketogenic diet. However, you should immediately eliminate the immune provoking and highly inflammatory foods discussed above.
It can be extremely difficult for an individual to go from hundreds of grams of carbohydrates a day to 50 or less on the standard ketogenic diet. If you are already on a low-carb diet, you can transition quicker than someone who is eating a higher carbohydrate diet.
For anyone new to a low-carb lifestyle, the best way to start is to replace the sugars, refined carbohydrates, grains and starches with healing root vegetables like sweet potatoes, beets, and carrots. You should also increase your healthy fat intake with the good fats listed above. By increasing your intake of healthy fats and decreasing your intake of carbohydrates, your body will adjust to this beneficial way of eating.
Tips for Being Successful on the Keto Autoimmune Diet
The following tips will help you be successful on the keto autoimmune diet:
- It is critical to stay very hydrated when on a ketogenic diet. Drink at least half of your body weight in water. Try to super hydrate first thing in the morning.
- Get plenty of sodium and minerals. On a low carbohydrate diet, your body will not retain sodium as it does on a high-carb diet. You will need to get plenty of sodium from generous amounts of pink Himalayan sea salt. Celery and cucumber are excellent low carb sources of natural sodium.
- Supplement with Betaine HCL, ox bile and digestive enzymes for proper digestion. We like to use BioGest with many of our clients. Also include MCT oil to support ketosis. MCT oil is refined from coconut oil and provides a readily absorbed source of ketones.
- It is important not to eat too much protein. Excess protein can drive more inflammation in the body.
- Make sure you are consuming enough calories, but not too many. Calorie restriction for a prolonged period can shift your body to a state of conservation and negatively affect hormone levels.
- Look to consume foods that support digestive health and stomach acid, bile and pancreatic enzyme production. The chart below has a number of these and we have mentioned many throughout this article.

Final Thoughts on the Keto Autoimmune Diet
Autoimmune conditions occur when the body’s immune system turns attacks the body’s own cells and tissues. There are many environmental causes of autoimmune conditions including gut dysfunction resulting from food sensitivities. A fantastic strategy for preventing and improving autoimmune conditions is implementing a keto autoimmune diet.
The keto autoimmune diet is a 6-week autoimmune elimination diet following ketogenic guidelines. After the 6-week elimination period, foods are slowly reintroduced/
The foods eliminated on this diet are pro-inflammatory foods as well as the most common immune provoking foods. These foods are replaced with healing foods including healthy fats, organic low-carbohydrate vegetables and low-glycemic fruits, herbs, grass-fed organic meats and eggs, and wild-caught fish.
The keto autoimmune diet can help with autoimmune conditions by decreasing inflammation and eliminating foods that may be triggering an immune response. This diet helps you identify foods to which you are sensitive and gives your body a chance to heal. Implementing the keto autoimmune diet is a powerful strategy for anyone with an autoimmune condition.

Are You Ready to Master the Keto Diet and End Inflammation?
Dr. Jockers has an amazing opportunity coming up… attend this free viewing event on the ketogenic diet beginning on January 21st.
The Keto Metabolic Breakthrough Masterclass covers a wealth of information about the health benefits of the ketogenic diet and how you can make this lifestyle change successfully. In these nine video lessons, you’ll learn how to harness the power of the keto diet to:
And, you’ll have Dr. Jockers as a guide to master how to get into ketosis without feeling hungry, deprived, or like you’re “dieting.
Burn fat and build lean body tissue…
Improve mental focus and concentration…
Improve blood sugar stability…
Reduce inflammation and pain…
Reduce your risk of chronic pain…
Want in? Follow This Link to reserve your spot in the Keto Metabolic Breakthrough Masterclass! Don’t wait, because the class is starting soon.*
FTC DISCLOSURE: Any health claims shared by viewers, students, friends, subscribers or clients are understood to be true and accurate, but are not verified in any way. Any products, programs, or personal recommendations made in this or any email communication from Revealed Films for 3rd parties will likely result in some form of compensation from said 3rd party. Always do your own due diligence and use your own judgment when making buying decisions and investments. Always consult a physician before making any health-related decisions. For more information click here for our terms of service.


